Fires can start from everyday activities like cooking, using electronics, or even lighting candles. Each fire, no matter how small, relies on three elements to burn: heat, fuel, and oxygen. This idea, known as the fire triangle, helps us understand how fires ignite and spread. Knowing this can save lives and prevent damage. For example, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) reports that cooking fires alone account for hundreds of daily emergencies.
When we explain the fire triangle, we also learn how to stop fires by removing one of its components. Whether it’s smothering flames or cooling with water, breaking the fire triangle is the key to fire safety. Services like N8 Fire Services provide tools and strategies based on this principle, ensuring homes and workplaces stay protected.
Understanding the fire triangle isn’t just for experts—it’s knowledge that everyone should have to keep their surroundings safe.
Fire Triangle Explain: Elements Necessary for Fire
Understanding how fires ignite and spread is an essential part of fire safety basics. Fires are not random events—they need specific conditions to occur. The concept of the fire triangle and its advanced form, the fire tetrahedron, simplifies these conditions into four critical elements: heat, oxygen, fuel, and a chemical chain reaction. By breaking one of these components, we can control or extinguish a fire effectively.
Let’s dive into the components of a fire triangle, explore fire safety strategies, and understand modern tools like the CO2 fire extinguisher to manage and prevent fires.
What Is the Fire Triangle?
The fire triangle is a simple model to understand how fires begin. Each fire needs:
- Heat to raise materials to their ignition point.
- Oxygen to sustain the combustion process.
- Fuel to keep the fire burning.
Without any one of these elements, fire cannot exist. The fire triangle explain model helps identify ways to disrupt fires at their source, making it a core principle in fire prevention strategies.
Heat: The Spark That Starts It All
The role of heat in combustion is fundamental. Heat is the energy source that raises a material’s temperature to its “flash point,” the level at which it ignites. Fires can start from common activities like:
- Cooking accidents (hot grease or overheated pans).
- Malfunctioning electronics generating sparks (Electrical Fire risks).
- Improperly extinguished candles.
Firefighters use fire control techniques like applying water to cool the burning material and lower its temperature below the ignition point. Recognizing sources of heat and eliminating them is the first step toward preventing fires.
Oxygen: Fire’s Invisible Lifeline
Every fire needs oxygen to thrive. In the oxygen in fire triangle model, it acts as a fuel for the combustion process, combining with heat and a flammable material to sustain the fire.
How oxygen sustains a fire:
- Oxygen reacts with fuel, producing carbon dioxide and heat.
- Open spaces with free airflow allow fires to spread faster.
To stop a fire, it’s essential to cut off oxygen by:
- Smothering the flames using a blanket or lid.
- Using a modern fire extinguisher like CO2 Fire Extinguishers, which interrupt the flow of oxygen while keeping the air breathable.
Understanding the relationship between heat, fuel, and oxygen can significantly reduce fire risks in homes and workplaces.
Fuel: The Element That Keeps Fires Burning
The fuel sources for fire are everywhere in our daily lives. From furniture and paper to cooking oils and gasoline, anything that burns can act as fuel. This is why fire can be challenging to stop—it often has abundant materials to sustain it.
Examples of fuel sources:
- Kitchen materials like oil and grease.
- Everyday items like paper, plastic, and textiles.
- Specialized materials like magnesium in industrial settings.
Removing fuel entirely can be difficult, but you can separate it from heat or oxygen to prevent a fire. For example, storing flammable materials away from heat sources is a simple but effective fire prevention strategy.
Beyond the Fire Triangle: The Fire Tetrahedron
While the fire triangle explain model includes heat, fuel, and oxygen, the fire tetrahedron adds a fourth crucial element: the chemical chain reaction. This reaction is the process that allows a fire to self-sustain.
- When heat, fuel, and oxygen combine, a series of chemical reactions release energy in the form of heat and light.
- These reactions continue until one element is removed or interrupted.
Modern fire extinguishing methods target this chain reaction. Advanced tools like Fire Extinguisher Foam or Element Fire Extinguishers release potassium ions that interrupt the reaction, effectively suffocating the fire without damaging the environment.
How Modern Fire Extinguishers Break the Fire Triangle
Traditional fire extinguishers were bulky and required frequent maintenance, but innovations like Element Fire Extinguishers make fire control more accessible. These compact devices use cutting-edge science to break the combustion process elements effectively.
How they work:
- Release free radical potassium ions.
- Disrupt the oxygen and fuel connection without depleting breathable air.
- Non-toxic and non-corrosive, making them safe for home and office use.
Unlike older extinguishers, these modern tools don’t expire and are portable, providing reliable solutions for a range of fires, including electrical fires and kitchen blazes. They align perfectly with modern firefighting strategies, ensuring safety with minimal effort.
Fire Classes and How to Tackle Them
Different fires require different approaches. The NFPA defines five fire extinguisher classes:
-
Class A
Ordinary combustibles (wood, paper, fabric).
- Use water or a multipurpose extinguisher.
-
Class B
Flammable liquids (oil, gasoline, paint).
- Smother flames or use chemical extinguishers like Fire Extinguisher Foam.
-
Class C
Electrical fires.
- De-energize and use non-conductive extinguishers.
-
Class D
Combustible metals (magnesium, titanium).
- Specialized extinguishers only.
-
Class K
Kitchen fires (cooking oils and fats).
- Use wet chemical extinguishers or smothering techniques.
Knowing these classes helps you apply the right fire control techniques for different emergencies.
Fire Safety Tips for Everyday Life
-
Store flammable items properly
Keep fuels like cooking oils or chemicals away from heat.
-
Install smoke detectors
Early warnings save lives.
-
Learn basic fire extinguishing methods
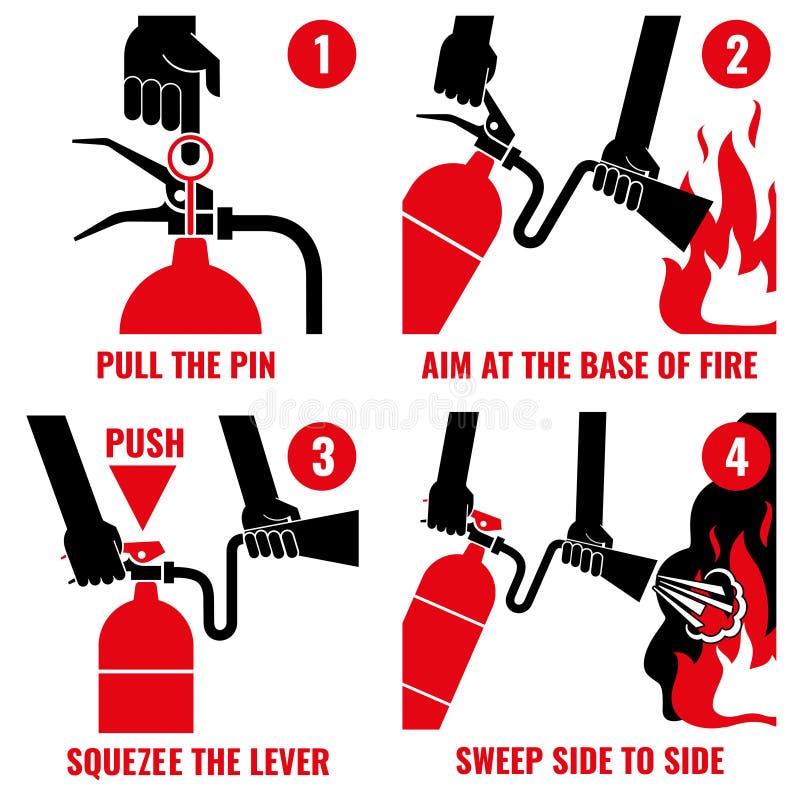
Understanding how to use a fire extinguisher by taking classes can make a big difference.
-
Practice wildfire prevention methods
Clear debris and keep fire-safe zones around properties.
Our expert offers practical strategies and tools to implement these tips effectively, ensuring your safety.
FAQS:
1.What is the fire element triangle symbol?
The Fire Tetrahedron, also known as the Triangle of Combustion, represents the fire triangle. It has a flame blazing in the center, with oxygen on the left, heat on the right, and fuel at the bottom. The relationship between the three components of fire is represented by this symbol.
2.How to break the fire triangle?
One of the fire triangle’s components can be eliminated in a number of ways, such by covering with mineral soil to remove oxygen, applying water to reduce heat, or building a fuel break in front of the fire to remove fuels.
3.What is another name for the fire tetrahedron?
The fire tetrahedron is frequently referred to as a fire triangle. Despite its similarities, the tetrahedron is more precise since it represents the chemical reaction’s fourth element.
4.How to interrupt the chemical chain reaction of fire?
To extinguish a fire, remove one element of the fire triangle or disrupt its chemistry. Free radical potassium ions alter oxygen molecules, stopping the combustion reaction while keeping the air breathable. This breaks the chemical chain, effectively starving the fire.
5.What are the elements of a fire triangle?
Oxygen, heat, and fuel are frequently referred to as the “fire triangle.”
Final Thoughts:
Understanding what the fire triangle explains is a simple yet powerful way to grasp how fires start and spread. By recognizing the roles of heat, oxygen, fuel, and the chemical chain reaction, we can take effective steps to prevent and control fires. Tools like modern fire extinguishers and services from experts like N8 Fire and safety Services make fire safety accessible for everyone. With this knowledge, you’re better prepared to protect your home, workplace, and loved ones from the dangers of fire. Stay informed, stay safe!
Protect your home and loved ones by understanding the fire triangle explanation model and using the right tools. Visit N8 Fire and Safety Services for expert fire safety solutions today!